smart card utility linux Chapter 7. Configuring smart card authentication using authselect. This section describes how to configure your smart card to achieve one of the following aims: The authselect tool configures . Newson's Electronics is reducing e-waste one repair at a time!If you want to .
0 · write certificate to smart card
1 · ubuntu smart card
2 · smart card based authentication
3 · smart card authentication step by
4 · smart card authentication
5 · read certificate from smart card
6 · linux smart card authentication
7 · 4.5.12 configure smart card authentication
An amiibo card, in this case, refers to an NFC card that some person has .
It can be used to configure smart card authentication on a Linux system by using the "smartcard" auth provider. And configure PAM (Pluggable Authentication Modules) to use SSSD for smart card authentication.
To enable smart card authentication we should rely on a module that allows PAM supported systems to use X.509 certificates to authenticate logins. The module relies on a PKCS#11 .
write certificate to smart card
ubuntu smart card
Overview. In this guide you’ll learn how to configure Smart Card authentication using SSSD as authentication daemon in a way that can be used both for user interface access via GDM login .Chapter 7. Configuring smart card authentication using authselect. This section describes how to configure your smart card to achieve one of the following aims: The authselect tool configures .Place the smart card into a reader or a USB port and supply the PIN code for the smart card instead of providing your password. This section describes what a smart card is and how .Abstract. With Red Hat Identity Management (IdM), you can store credentials in the form of a private key and a certificate on a smart card. You can then use this smart card instead of .
We configure PAM to enforce smart card authentication in addition to the standard password prompt as second factor authentication. You need to have a smart card (with valid . The generate-keypair, import-object, export-object and delete-object subcommands can be used for easy management of keys and certificates on a PKCS#11 . ACS QuickView v2.13 (For Linux OS) This tool has the functionality to read and display the smart card reader and the smart card details. This tool also serves as a polling tool that . It can be used to configure smart card authentication on a Linux system by using the "smartcard" auth provider. And configure PAM (Pluggable Authentication Modules) to use SSSD for smart card authentication.
To enable smart card authentication we should rely on a module that allows PAM supported systems to use X.509 certificates to authenticate logins. The module relies on a PKCS#11 library, such as opensc-pkcs11 to access the smart card for the credentials it will need.Overview. In this guide you’ll learn how to configure Smart Card authentication using SSSD as authentication daemon in a way that can be used both for user interface access via GDM login and unlock and also some basic principles that are common to headless setups.OpenSC provides an optional set of libraries and utilities to work with smart cards using pcsclite. Install opensc. If the card reader does not have a PIN pad, append the line (s) and set enable_pinpad = false in the opensc configuration file /etc/opensc.conf.
Chapter 7. Configuring smart card authentication using authselect. This section describes how to configure your smart card to achieve one of the following aims: The authselect tool configures user authentication on Linux hosts and you can use .Place the smart card into a reader or a USB port and supply the PIN code for the smart card instead of providing your password. This section describes what a smart card is and how smart card authentication works. It describes the tools that you .Abstract. With Red Hat Identity Management (IdM), you can store credentials in the form of a private key and a certificate on a smart card. You can then use this smart card instead of passwords to authenticate to services. Administrators can configure mapping rules to reduce the administrative overhead.
We configure PAM to enforce smart card authentication in addition to the standard password prompt as second factor authentication. You need to have a smart card (with valid keys) and a PKCS#11 module to read your card (either OpenSC or one from card’s vendor). The generate-keypair, import-object, export-object and delete-object subcommands can be used for easy management of keys and certificates on a PKCS#11 token. P11-kit tool now also supports management of PKCS#11 profiles with add-profile, delete-profile and list-profiles subcommands.ACS QuickView v2.13 (For Linux OS) This tool has the functionality to read and display the smart card reader and the smart card details. This tool also serves as a polling tool that checks the presence and absence of the card in a reader. It can be used to configure smart card authentication on a Linux system by using the "smartcard" auth provider. And configure PAM (Pluggable Authentication Modules) to use SSSD for smart card authentication.
smart card based authentication
To enable smart card authentication we should rely on a module that allows PAM supported systems to use X.509 certificates to authenticate logins. The module relies on a PKCS#11 library, such as opensc-pkcs11 to access the smart card for the credentials it will need.Overview. In this guide you’ll learn how to configure Smart Card authentication using SSSD as authentication daemon in a way that can be used both for user interface access via GDM login and unlock and also some basic principles that are common to headless setups.OpenSC provides an optional set of libraries and utilities to work with smart cards using pcsclite. Install opensc. If the card reader does not have a PIN pad, append the line (s) and set enable_pinpad = false in the opensc configuration file /etc/opensc.conf.Chapter 7. Configuring smart card authentication using authselect. This section describes how to configure your smart card to achieve one of the following aims: The authselect tool configures user authentication on Linux hosts and you can use .
Place the smart card into a reader or a USB port and supply the PIN code for the smart card instead of providing your password. This section describes what a smart card is and how smart card authentication works. It describes the tools that you .Abstract. With Red Hat Identity Management (IdM), you can store credentials in the form of a private key and a certificate on a smart card. You can then use this smart card instead of passwords to authenticate to services. Administrators can configure mapping rules to reduce the administrative overhead.
We configure PAM to enforce smart card authentication in addition to the standard password prompt as second factor authentication. You need to have a smart card (with valid keys) and a PKCS#11 module to read your card (either OpenSC or one from card’s vendor).
The generate-keypair, import-object, export-object and delete-object subcommands can be used for easy management of keys and certificates on a PKCS#11 token. P11-kit tool now also supports management of PKCS#11 profiles with add-profile, delete-profile and list-profiles subcommands.


smart card authentication step by
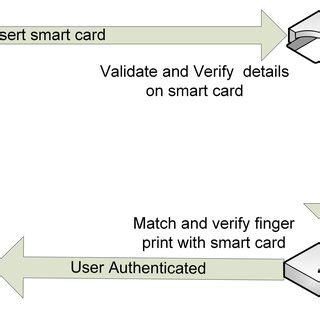
smart card authentication
read certificate from smart card
linux smart card authentication
Available memory: the actual memory you have to write data to the NFC Tag. URL length: .I found out this guide which was quite helpful. In below it covers the Memory block structure: 1K Cards - 16 sectors of 4 blocks each (sectors 0..15) 4K Cards - 32 sectors of 4 blocks each (sectors 0..31) and 8 sectors of 16 blocks each .
smart card utility linux|smart card authentication step by